ATD Blog
Assessing Online Collaborative Learning
Thu Apr 28 2016

Content
One of the most common concerns about the evaluation of collaborative learning is that even though all participants do not contribute equally, their efforts are grouped with those of their team members in a single score.
One of the most common concerns about the evaluation of collaborative learning is that even though all participants do not contribute equally, their efforts are grouped with those of their team members in a single score.
Content
A solution to this genuine concern is to assess participants at both the individual and group level. Additionally, as recommended in the previous post in this series , group rewards should be based on individual learning. This reward interdependence helps emphasize individual accountability. It also compels participants to support the learning process of their team members.
A solution to this genuine concern is to assess participants at both the individual and group level. Additionally, as recommended in the previous post in this series, group rewards should be based on individual learning. This reward interdependence helps emphasize individual accountability. It also compels participants to support the learning process of their team members.
Content
When is the right time to evaluate a collaborative learning program? The assessment of the transformation in knowledge (cognitive domain) or social behavior (affective domain) should be done throughout the collaborative process, while keeping the participants motivated, and not just toward the end.
When is the right time to evaluate a collaborative learning program? The assessment of the transformation in knowledge (cognitive domain) or social behavior (affective domain) should be done throughout the collaborative process, while keeping the participants motivated, and not just toward the end.
Content
Assessing the progress at multiple stages of the program helps identify:
Assessing the progress at multiple stages of the program helps identify:
Content
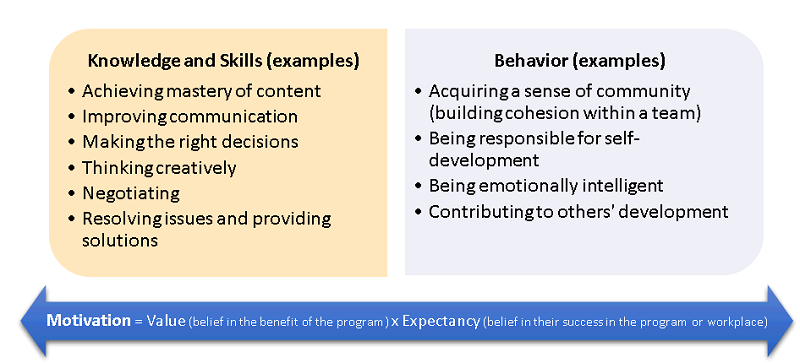
desired improvements in knowledge, skills, and behavior
desired improvements in knowledge, skills, and behavior
Content
challenges or conflicts
challenges or conflicts
Content
required changes to the flow of the program
required changes to the flow of the program
Content
·necessary checkpoints.
·necessary checkpoints.
Content
Checkpoints should be spaced out in such a way that participants have enough time to reflect on their performance and devise a strategy for subsequent collaborative sessions to improve their performance. This approach will help them develop the necessary skills and behavior for effective collaboration.
Checkpoints should be spaced out in such a way that participants have enough time to reflect on their performance and devise a strategy for subsequent collaborative sessions to improve their performance. This approach will help them develop the necessary skills and behavior for effective collaboration.
Content
An assessment will vary depending on three key elements:
An assessment will vary depending on three key elements:
Content
#1: Focus
#1: Focus
Content
Knowledge
Knowledge
Content
Skills
Skills
Content
Behavior
Behavior
Content
#2: Type:
#2: Type:
Content
Self-assessment
Self-assessment
Content
Team self-assessment
Team self-assessment
Content
Peer assessment ( Tip: If evaluators are hard-pressed for time to grade a session, use peer rating to reduce the evaluators’ workload while keeping participants engaged.)
Peer assessment (Tip: If evaluators are hard-pressed for time to grade a session, use peer rating to reduce the evaluators’ workload while keeping participants engaged.)
Content
Assessment by facilitator
Assessment by facilitator
Content
Assessment by sponsor(s)
Assessment by sponsor(s)
Content
#3: Format
#3: Format
Content
Questionnaires
Questionnaires
Content
Critical thinking assignments
Critical thinking assignments
Content
Reflective summary
Reflective summary
Content
Online research reports
Online research reports
Content
Online survey
Online survey
Content
Virtual role plays
Virtual role plays
Content
Scenario-based questions
Scenario-based questions
Content
Rating scales
Rating scales
Content
Feedback forms ( Tip: When collecting feedback on session expectation fulfillment, do not stop after evaluating it only once. Try to gather participants’ opinions using the “step-back-dive-in” approach throughout the program, to be aware of participants’ motivation levels and adjust program activities, if required.)
Feedback forms (Tip: When collecting feedback on session expectation fulfillment, do not stop after evaluating it only once. Try to gather participants’ opinions using the “step-back-dive-in” approach throughout the program, to be aware of participants’ motivation levels and adjust program activities, if required.)
Content
From the various assessment formats listed above, data can be collected in the form of:
From the various assessment formats listed above, data can be collected in the form of:
Content
individual or group activity outputs
individual or group activity outputs
Content
ratings by facilitators, peers, team members, and individuals
ratings by facilitators, peers, team members, and individuals
Content
feedback by facilitators, peers, and team members
feedback by facilitators, peers, and team members
Content
recorded interactions or log files, such as discussion forums, chats, whiteboard activities, videos, audio files, and transcripts
recorded interactions or log files, such as discussion forums, chats, whiteboard activities, videos, audio files, and transcripts
Content
change reports or periodical digests from the online learning environment or software.
change reports or periodical digests from the online learning environment or software.
Content
These data can be collected and managed through the learning environment itself. For example, RSS feeds can help facilitators monitor group activities and indicate when to intervene. Additionally, digital footprints can track participant or group activity. Such advances in digital tracking, data collection, and monitoring tools reduce the task of managing data for multiple groups. Moreover, if relevant data, such as contribution summaries in various discussion threads, new discussions, or top contributors, are available to participants, they feel motivated to contribute and collaborate further.
These data can be collected and managed through the learning environment itself. For example, RSS feeds can help facilitators monitor group activities and indicate when to intervene. Additionally, digital footprints can track participant or group activity. Such advances in digital tracking, data collection, and monitoring tools reduce the task of managing data for multiple groups. Moreover, if relevant data, such as contribution summaries in various discussion threads, new discussions, or top contributors, are available to participants, they feel motivated to contribute and collaborate further.
Content
By analyzing data from multiple sources throughout a collaborative learning program, we can guide a group or an individual on improving performance through constructive (written or verbal) feedback. A thorough assessment of data, which can be archived and retrieved later, also helps determine the effectiveness of an online collaboration program and the learning environment.
By analyzing data from multiple sources throughout a collaborative learning program, we can guide a group or an individual on improving performance through constructive (written or verbal) feedback. A thorough assessment of data, which can be archived and retrieved later, also helps determine the effectiveness of an online collaboration program and the learning environment.
Content
This employee-oriented approach of learning is beneficial for organizations on multiple fronts. It provides hands-on experience in working with peers globally, learning from the success and failures of working together, and making things work when working toward a common outcome or goal. It also supports cross-cultural preferences in large organizations, leading to efficacy in operations.
This employee-oriented approach of learning is beneficial for organizations on multiple fronts. It provides hands-on experience in working with peers globally, learning from the success and failures of working together, and making things work when working toward a common outcome or goal. It also supports cross-cultural preferences in large organizations, leading to efficacy in operations.
Content
However, to sustain a collaborative learning environment, it is important that an organization’s leadership accepts it, communicates its value, drives the learning culture, and supports its implementation. This is crucial in forming a knowledge-based global workforce, which leads to shorter time to efficiency and keeps an organization ahead of its competitors.
However, to sustain a collaborative learning environment, it is important that an organization’s leadership accepts it, communicates its value, drives the learning culture, and supports its implementation. This is crucial in forming a knowledge-based global workforce, which leads to shorter time to efficiency and keeps an organization ahead of its competitors.
